12/5—Moderna vaccine provides immunity for 119+ days
Durability of Responses after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 Vaccination [Moderna]
We describe immunogenicity data 119 days after the first vaccination in 34 healthy adult participants in the same trial who received two injections of vaccine at a dose of 100 μg. [These] produced high levels of binding and neutralizing antibodies that declined slightly over time, as expected, but they remained elevated in all participants 3 months after the booster vaccination. No serious adverse events were noted in the trial.
Placebo-Controlled Trials of Covid-19 Vaccines — Why We Still Need Them
After relatively short follow-up in phase 3 trials, even when vaccine efficacy appears to be high, reliable information will still be needed on longer-term safety and duration of protection. Other information gaps will include more comprehensive assessments of short-term safety, knowledge of whether waning of vaccine-induced protection may lead to vaccine-enhanced disease if a vaccinee becomes infected on exposure to SARS-CoV-2, information on protection against clinically severe forms of Covid-19, and knowledge of any associations between the degree of protection and the recipient’s age or coexisting conditions.
Preexisting and de novo humoral immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in humans
SARS-CoV-2 S-reactive IgG antibodies were detected by flow cytometry in 5 of 34 SARS-CoV-2-uninfected individuals with RT-qPCR-confirmed Human coronavirus infection, as well as in 1 of 31 individuals without recent Human coronavirus infection. This suggested that cross-reactivity may have persisted from earlier Human coronavirus infections, rather than having been induced by the most recent one.
Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 on mink farms between humans and mink and back to humans
We describe an in-depth investigation using whole genome sequencing of outbreaks on 16 mink farms and the humans living or working on these farms. We conclude that the virus was initially introduced from humans and has since evolved, most likely reflecting widespread circulation among mink in the beginning of the infection period several weeks prior to detection. Despite enhanced biosecurity, early warning surveillance and immediate culling of infected farms, transmission occurred between mink farms in three big transmission clusters with unknown modes of transmission. Sixty-eight percent (68%) of the tested mink farm residents, employees and/or contacts had evidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Where whole genomes were available, these persons were infected with strains with an animal sequence signature, providing evidence of animal to human transmission of SARS-CoV-2 within mink farms.
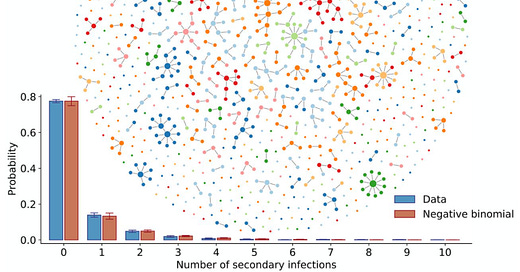
Transmission heterogeneities, kinetics, and controllability of SARS-CoV-2
Based on detailed patient and contact tracing data in Hunan, China we find 80% of secondary infections traced back to 15% of SARS-CoV-2 primary infections, indicating substantial transmission heterogeneities. Transmission risk scales positively with the duration of exposure and the closeness of social interactions and is modulated by demographic and clinical factors.

Get it by email:
Missed an update? View past issues.